Nonreflecting Boundary Kernels
The exact nonreflecting boundary conditions are derived from separation
of variables in rectangular, cylindrical, or spherical coordinate systems.
Under this separation, the boundary condition for each wavenumber is
independent of the others, and depends on its own history by a convolution.
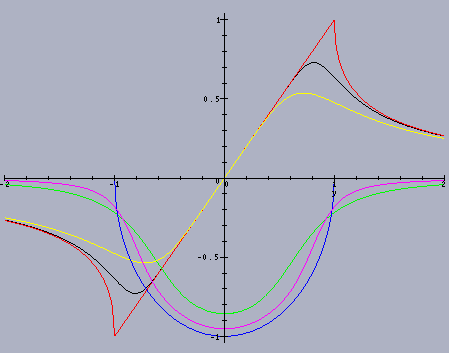
The convolution kernels in the Laplace domain for three different
wavenumbers are shown in the plot below.
The plot shows the real and imaginary parts of the kernels on the imaginary
axis. (For each, the real part is even.) The simplicity of these kernels
leads their efficient approximation as rational functions, with controlled
(arbitrarily small) error.
Back to Time-Domain Algorithms for Computational Electromagnetics
Bradley K Alpert
Last modified: Fri Jul 14 12:11:53 MDT 2000