
Overview
The application mmGraph provides a data display service similar to
that of mmDataTable. The usual
data source is a running solver, but rather than the textual output
provided by mmDataTable, mmGraph produces 2D line plots.
mmGraph also stores the data it receives, so it can produce
multiple views of the data and can save the data to disk. Postscript
output is also supported.
Launching
mmGraph may be started either by selecting the mmGraph
button on mmLaunch or from the command
line via
tclsh oommf.tcl mmGraph [standard options] [-net <0|1>] [loadfile ...]
Inputs
Input to mmGraph may come from either a file in the
ODT format,
or when -net 1 (the default) is active, from a client application
(typically a running solver). The
File|Open... dialog box is used to select an input file.
Receipt of data from client applications is the same as for
mmDataTable. In either
case, input data are appended to any previously held data.
When reading from a file, mmGraph will automatically decompress data using the local customization ``Nb_InputFilter decompress'' option to Oc_Option. For details, see the discussion on file translation in the Inputs section of the mmDisp documentation.
Curve breaks (i.e., separation of a curve into disjoint segments) are recorded in the data storage buffer via curve break records. These records are generated whenever a new data table is detected by mmGraph, or when requested by the user using the mmGraph Options|Break Curves menu option.
Outputs
Unlike mmDataTable, mmGraph internally stores the data sent to it. These data may be written to disk via the File|Save As... dialog box. If the file specified already exists, then mmGraph output is appended to that file. The output is in the tabular ODT format. The data are segmented into separate Table Start/Table End blocks across each curve break record.
By default, all data currently held by mmGraph is written, but the Save: Selected Data option presented in the File|Save As... dialog box causes the output to be restricted to those curves currently selected for display. In either case, the graph display limits do not affect the output.
The save operation writes records that are held by mmGraph at the time the File|Save As... dialog box OK button is invoked. Additionally, the Auto Save option in this dialog box may be used to automatically append to the specified file each new data record as it is received by mmGraph. The appended fields will be those chosen at the time of the save operation, i.e., subsequent changing of the curves selected for display does not affect the automatic save operation. The automatic save operation continues until either a new output file is specified, the Options|Stop Autosave control is invoked, or mmGraph is terminated.
The File|Print... dialog is used to produce a Postscript file of the current graph. On Unix systems, the output may be sent directly to a printer by filling the Print to: entry with the appropriate pipe command, e.g., |lpr. (The exact form is system dependent.)
Controls
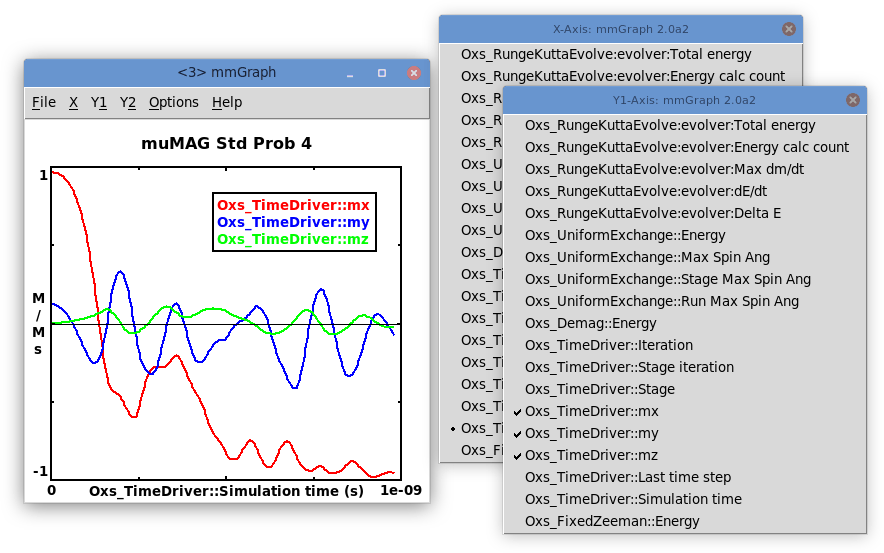
Graphs are constructed by selecting any one item off the
X-axis menu, and any number of items off the Y1-axis and
Y2-axis menus. The y1-axis is marked on the left side of the
graph; the y2-axis on the right. These menus may be detached by
selecting the dashed rule at the top of the list. Sample results are
shown in the figure at the start of this section.
When mmGraph is first launched, all the axis menus are empty. They are dynamically built based on the data received by mmGraph. By default, the graph limits and labels are automatically set based on the data. The x-axis label is set using the selected item data label and measurement unit (if any). The y-axes labels are the measurement unit of the first corresponding y-axis item selected.
The Options|Configure... dialog box allows the user to override default settings. To change the graph title, simply enter the desired title into the Title field. To set the axis labels, deselect the Auto Label option in this dialog box, and fill in the X Label, Y1 Label and Y2 Label fields as desired. The axis limits can be set in a similar fashion. In addition, if an axis limit is left empty, a default value (based on all selected data) will be used. Select the Auto Scale option to have the axis ranges automatically adjust to track incoming data.
Use the Auto Offset Y1 and Auto Offset Y2 to automatically translate each curve plotted against the specified axis up or down so that the first point on the curve has a y-value of zero for a linear axis or one for a logarithmic axis. This feature is especially useful for comparing variations between different energy curves, because for these curves one is typically interested in changes is values rather than the absolute energy value itself.
By default the scaling on each axis is linear. The Log scale axes check boxes enables logarithmic scaling on the selected axes. If logarithmic scaling is selected then any point with a zero value is dropped and negative values are replaced with their corresponding positive absolute value.
The size of the margin surrounding the plot region is computed automatically. Larger margins may be specified by filling in the appropriate fields in the Margin Requests section. Units are pixels. Requested values smaller than the computed (default) values are ignored.
The Canvas color selection sets the color of the canvas background. The curve colors and symbol types are automatically assigned, either by curve or segment, as specified by the Color selection control. (Data collected across multiple solver runs will consist of one segment for each run.) The Display control can be used to enable or disable display of curves and/or symbols.
The initial curve width is determined by the Ow_GraphWin default_curve_width setting in the config/options.tcl and config/local/options.tcl files, following the usual method of local customization. The current curve width can be changed by specifying the desired width in the Curve Width entry in the Options|Configure... dialog box. The units are pixels. Long curves will be rendered more quickly, especially on Windows, if the curve width is set to 1. The symbol frequency and size (in pixels) may also be controlled. A value of 0 for Symbol Freq disables symbol display. The default values for these options can be controlled from the configuration options.tcl files.
As mentioned earlier, mmGraph stores in memory all data it receives. Over the course of a long run, the amount of data stored can grow to many megabytes. This storage can be limited by specifying a positive (> 0) value for the Point buffer size entry in the Options|Configure... dialog box. The oldest records are removed as necessary to keep the total number of records stored under the specified limit. A zero value for Point buffer size is interpreted as no limit. (The storage size of an individual record depends upon several factors, including the number of items in the record and the version of Tcl being used.) Data erasures may not be immediately reflected in the graph display.
At any time, the point buffer storage may be completely emptied with Options|Clear Data, or thinned via Options|Thin Data. The Options|Stop Autosave selection will turn off the auto save feature, if currently active. The Options|Break Curves item inserts a curve break record into the point buffer, causing a break in each curve after the current point. This option may be useful if mmGraph is being fed data from multiple sources.
Also on this menu is Options|Rescale, which autoscales the graph axis limits from the selected data. This command ignores but does not reset the Auto Scale setting in the Options|Configure... dialog box. The Rescale command may also be invoked by pressing the Home key.
The Options|Key selection toggles the key (legend) display on and off. The key may also be repositioned by dragging with the left mouse button. If curves are selected off both the y1 and y2 menus, then a horizontal line in the key separates the two sets of curves, with the labels for the y1 curves on top.
If the Options|Auto Reset selection is enabled, then when a new table is detected all previously existing axis menu labels that are not present in the column list of the new data set are deleted, along with their associated data. mmGraph will detect a new table when results from a new problem are received, or when data is input from a file. If Options|Auto Reset is not selected, then no data or axis menu labels are deleted, and the axes menus will show the union of the old column label list and the new column label list. If the axes menus grow too long, the user may manually apply the File|Reset command to clear them.
The last command on the options menu is Options|Smooth. If smoothing is disabled, then the data points are connected by straight line segments. If enabled, then each curve is rendered as a set of parabolic splines, which do not in general pass through the data points. This is implemented using the -smooth 1 option to the Tcl canvas create line command; see that documentation for details.
A few controls are available only using the mouse. If the mouse pointer is positioned over a drawn item in the graph, holding down the Ctrl key and the left mouse button will bring up the coordinates of that point, with respect to the y1-axis. Similarly, depressing the Ctrl key and the right mouse button, or alternatively holding down the Ctrl+Shift keys while pressing the left mouse button will bring up the coordinates of the point with respect to the y2-axis. The coordinates displayed are the coordinates of a point on a drawn line, which are not necessarily the coordinates of a plotted data point. (The data points are plotted at the endpoints of each line segment.) The coordinate display is cleared when the mouse button is released while the Ctrl key is down.
One vertical and one horizontal rule (line) are also available. Initially, these rules are tucked and hidden against the left and bottom graph axes, respectively. Either may be repositioned by dragging with the left or right mouse button. The coordinates of the cursor are displayed while dragging the rules. The displayed y-coordinate corresponds to the y1-axis if the left mouse button is used, or the y2-axis if the right mouse button or the Shift key with the left mouse button are engaged.
The graph extents may be changed by selecting a ``zoom box'' with the mouse. This is useful for examining a small portion of the graph in more detail. This feature is activated by clicking and dragging the left or right mouse button. A rectangle will be displayed that changes size as the mouse is dragged. If the left mouse button is depressed, then the x-axis and y1-axis are rescaled to just match the extents of the displayed rectangle. If the right mouse button, or alternatively the shift key + left mouse button, is used, then the x-axis and y2-axis are rescaled. An arrow is drawn against the rectangle indicating which y-axis will be rescaled. The rescaling may be canceled by positioning the mouse pointer over the initial point before releasing the mouse button. The zoom box feature is similar to the mouse zoom control in the mmDisp application, except that here there is no ``un-zooming'' mouse control. However, the coordinate limits for each zoom are stored in a list, and the Esc and Shift+Esc keys may be used to move backwards and forwards, respectively, through this list. The Enter/Return key will copy the current coordinate limits to the list. A pointer is kept to the selected display configuration state, and new states are added after that point; if a display state is added in the interior of the list (i.e. ahead of the last state), then all configurations following the new entry are deleted. The entire list is cleared any time automatic scaling is invoked.
The Page Up and Page Down keys may also be used to zoom the display in and out. Use in conjuction with the Shift key to jump by larger steps, or with the Ctrl key for finer control. The Options|Rescale command or the Options|Configure... dialog box may also be used to reset the graph extents.
If mmGraph is being used to display data from a running solver, and if Auto Scale is selected in the Options|Configure... dialog box, then the graph extents may be changed automatically when a new data point is received. This is inconvenient if one is simultaneously using the zoom feature to examine some portion of the graph. In this case, one might prefer to disable the Auto Scale feature, and manually pan the display using the keyboard arrow keys. Each key press will translate the display one half frame in the indicated direction. The Shift key used in combination with an arrow keys double the pan step size, while the Ctrl key halves it.
The menu selection File|Reset reinitializes the mmGraph application to its original state, releasing all data and clearing the axis menus. The menu selection File|Exit terminates the application. The menu Help provides the usual help facilities.
Details
The axes menus are configured based on incoming data. As a result,
these menus are initially empty. If a graph widget is scheduled to
receive data only upon control point or stage done events in the solver,
it may be a long time after starting a problem in the solver before the
graph widget can be configured. Because mmGraph keeps all data up
to the limit imposed by the Point buffer size, data loss is usually
not a problem. Of more importance is the fact that automatic data
saving can not be set up until the first data point is
received. As a workaround, the solver initial state may be sent
interactively as a dummy point to initialize the graph widget axes
menus. Select the desired quantities off the axes menus, and use the
Options|clear Data command to remove the dummy point from
mmGraph's memory. The File|Save As... dialog box may
then be used--with the Auto Save option enabled--to write out
an empty table with proper column header information. Subsequent data
will be written to this file as they arrive.