The numerical solution of partial differential equations (PDEs) is often the most computationally intensive part of solving mathematical models of physical phenomena important to industry. For this reason, much research has been performed to find faster methods to solve PDEs at higher resolution. A recent development involves the combination of solution-adapted unstructured grids, to provide higher resolution only where it is needed, with multi-level (multigrid) linear system solution techniques, which have the smallest possible asymptotic operation counts. These adaptive multi-level methods have been shown to be effective on sequential computers, but their use on parallel computers is in the early stage of research.
We have been investigating methods of this type for several years. As part of this research, a new method was developed and implemented in an experimental sequential code called MGGHAT (MultiGrid Galerkin Hierarchical Adaptive Triangles), which has been released to the public, is seeing widespread use, and was selected as a finalist for the 1995 Wilkinson Prize for Numerical Software. As part of NIST's efforts in High Performance Computing and Communications (HPCC) and the Scalable Computing Testbed project of the CAML High Performance Systems and Services Division, a new parallel adaptive multilevel method, based on MGGHAT, is being developed and implemented in a Fortran 90 program, PHAML (Parallel Hierarchical Adaptive MultiLevel).
The major accomplishments in the past year are:

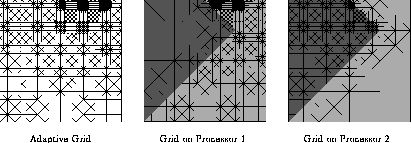
Caption: Full Domain Partition of an adaptive grid over two processors.