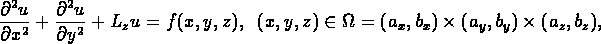
Roldan Pozo, ACMD
Karin A. Remington, Scientific Computing Environments Division
This project has been focused on developing and analyzing the performance characteristics of fast three-dimensional elliptic solvers on parallel architectures such as the IBM SP2, Connection Machine CM-5, and Intel iPSC/860. Developing efficient implementations is challenging, due to required global ``all-to-all'' communication traffic, which occurs primarily in multidimensional array transpositions, and improvements over existing implementations is a continuing area of research.
The problem class considered in this project is elliptic partial differential equations of the form
where
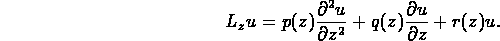
Equations of this form frequently arise in large-scale modeling of
physical and chemical processes.
The communication requirements for parallel Fourier solvers
such as those considered in this project are among the most demanding
possible in terms of bandwidth and communication latency.
The communication to computation ratio (one measure of the amount of
overhead on a parallel computer) becomes increasingly unfavorable as
problem size increases:
for a three dimensional domain with 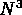 points, the ratio is
points, the ratio is 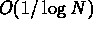 .
These communication patterns are taxing for some architectures.
Nevertheless, such applications serve as a valuable
tool to identify bottlenecks in a physical networks and
message passing layers.
.
These communication patterns are taxing for some architectures.
Nevertheless, such applications serve as a valuable
tool to identify bottlenecks in a physical networks and
message passing layers.