
READ_WATCH
reads the values from a StopWatch
watch
SYNOPSIS
subroutine read_watch (read_result, watch, clock, err)
DESCRIPTION
Returns the value of the specified clocks from the specified watches. The
result is returned in
read_result
. Clocks can be read regardless of whether they are
running, stopped or paused.
One or more watches must be specified. The argument watch can be a single variable of type watchtype (see stopwatch(3)) to read one watch, or an array of type watchtype to read several watches. watch can not be a watchgroup because there is no natural order of the watches in the group to use in constructing an array for the result.
The optional argument clock specifies which clocks to read from the specified watch(es). If omitted, the current default clocks (see option_stopwatch(3)) are read. If present, clock must be a character string containing 'cpu', 'user', 'sys', or 'wall', or an array of such character strings.
The type of read_result
must agree with the form of the arguments
watch
and clock:


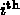 entry of the result is the
specified clock value on watch(i).
entry of the result is the
specified clock value on watch(i).

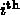 entry of the result is the value in clock(i)
on the
specified watch.
In the case that clock
is omitted, note that
the default clocks specify the contents of the result, and the default clocks
can be determined using inquiry_stopwatch(3).
entry of the result is the value in clock(i)
on the
specified watch.
In the case that clock
is omitted, note that
the default clocks specify the contents of the result, and the default clocks
can be determined using inquiry_stopwatch(3).

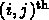 entry of the
result is the value in clock(j)
on watch(i).
entry of the
result is the value in clock(j)
on watch(i).
If read_result is a pointer to an array, it will be allocated by read_watch , and should be deallocated after use to avoid memory leakage.
DIAGNOSTICS
If present, the optional intent OUT integer argument err
returns
a status code. The code is the sum of the values listed below.
An error message will be printed to a specified I/O unit (unit 6 by default) if print_errors is TRUE (default is TRUE). The error message contains more detail about the cause of the error than can be obtained from just the status code, so you should set print_errors to TRUE if you have trouble determining the cause of the error.
If abort_errors is TRUE (default is FALSE), the program will terminate on an error condition. Otherwise, the program will continue execution but the watch(es) will not be read.
See option_stopwatch(3) for further information on print_errors, abort_errors and I/O units.
The relevant status codes and messages are:
In addition to the run time diagnostics generated by StopWatch
, the following
problem may arise:

EXAMPLES
type (watchtype) w1, w2(3)
real x
real, pointer :: y(:), z(:,:)
integer errcode
call read_watch(x, w1, 'user')
call read_watch(y, w1, err=errcode)
call read_watch(z, w2, (/'cpu ', 'wall'/), errcode)
deallocate(y, z)
The first call reads the user clock on a single watch. The second call reads the default clocks on a single watch and returns a status code. y is allocated with dimension equal to the number of default clocks. The third call reads the cpu and wall clocks from three watches given as an array and returns a status code. The deallocate statement frees the memory allocated in read_watch .
BUGS
It cannot be determined whether or not a watch variable or
watch group has been created (passed
as an argument to create_watch
or create_watchgroup).
If
a watch or watch group that has never been created
is passed into read_watch,
it might
generate a Fortran error due to passing a pointer with undefined association
status to the Fortran intrinsic function associated.
Some compilers
will allow this as an extension to the Fortran 90 standard and recognize that
the pointer is not associated, in which case the ``Watch needs to be created''
error message is generated.