

Overview
The application Oxsii is the graphical, interactive user interface
to the Oxs micromagnetic computation engine. Within the
OOMMF architecture, Oxsii is both a server and a client
application. Oxsii is a client of data table display and storage
applications, and vector field display and storage applications.
Oxsii is the server of a solver control service for which the only
client is mmLaunch. It is through
this service that mmLaunch provides a user interface window (shown
above) on behalf of Oxsii.
A micromagnetic problem is communicated to Oxsii via a MIF 2 file, which defines a collection of Oxs_Ext objects that comprise the problem model. The problem description includes a segmentation of the lifetime of the simulation into stages. Stages mark discontinuous changes in model attributes, such as applied fields, and also serve to mark coarse grain simulation progress. Oxsii provides controls to advance the simulation, stopping between iterations, between stages, or only when the run is complete. Throughout the simulation, the user may save and display intermediate results, either interactively or via scheduling based on iteration and stage counts.
Problem descriptions in the MIF 1.1 and MIF 1.2 formats can also be input. They are automatically passed to mifconvert for implicit conversion to MIF 2 format.
Launching
Oxsii may be started either by selecting the
Oxsii button on mmLaunch, or from the
command line via
tclsh oommf.tcl oxsii [standard options] [-exitondone <0|1>] \ [-nice <0|1>] [-parameters params] [-pause <0|1>] \ [-restart <0|1>] [-threads <count>] [-numanodes <nodes>] [miffile]where
-parameters "A 13e-12 Ms 800e3"could be used to set A to 13e-12 and Ms to 800e3. The quoting mechanism is shell/operating system specific; refer to your system documentation for details.
The default value for nodes is ``none'', which allows the operating system to assign and move threads based on overall system usage. This is also the behavior obtained when the Oxs build is not NUMA-aware. On the other hand, if a machine is dedicated primarily to running one instance of Oxsii, then Oxsii will likely run fastest if the thread count is set to the number of processing cores on the machine, and nodes is set to ``auto''. If you want to run multiple copies of Oxsii simultaneously, or run Oxsii in parallel with some other application(s), then set the thread count to a number smaller than the number of processing cores and restrict Oxsii to some subset of the memory nodes with the -numanodes option and an explicit nodes list.
The environment variable OOMMF_NUMANODES may be used to override the default ``none'' setting, but is subordinate to the command line setting, if any.
Since Oxsii does not present any user interface window of its own, it depends on mmLaunch to provide an interface on its behalf. The entry for an instance of Oxsii in the Threads column of any running copy of mmLaunch has a checkbutton next to it. This button toggles the presence of a user interface window through which the user may control that instance of Oxsii.
Inputs
Unlike mmSolve2D,
Oxsii loads problem specifications
directly from disk (via the File|Load... menu selection),
rather than through
mmProbEd or
FileSource. Input files for Oxsii must be either
in the MIF 2
format, or convertible to that format by the command line tool
mifconvert. There are sample MIF 2 files in the
directory oommf/app/oxs/examples. MIF files may be edited with
any plain text editor.
Outputs
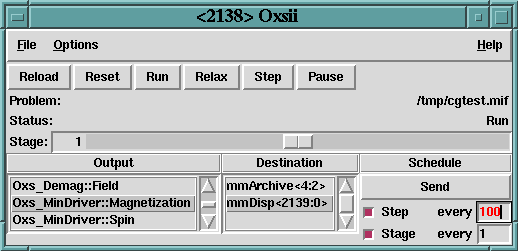
Once a problem has been loaded, the scroll box under the Output
heading will fill with a list of available outputs. The contents of
this list will depend upon the Oxs_Ext objects specified in the
input MIF file. Refer to the documentation for those objects for
specific details.
To send output from Oxsii to another OOMMF application, highlight the
desired selection under the Output heading, make the corresponding
selection under the Destination heading, and then specify the output
timing under the Schedule heading. Outputs may be scheduled by the
step or stage, and may be sent out interactively by pressing the
Send button. The initial output configuration is set by
Destination and
Schedule commands in the input
MIF file.
Outputs fall under two general categories: scalar (single-valued) outputs and vector field outputs. The scalar outputs are grouped together as the DataTable entry in the Output scroll box. Scalar outputs include such items as total and component energies, average magnetization, stage and iteration counts, max torque values. When the DataTable entry is selected, the Destination box will list all OOMMF applications accepting datatable-style input, i.e., all currently running mmDataTable, mmGraph, and mmArchive processes.
The vector field outputs include pointwise magnetization, various total and partial magnetic fields, and torques. Unlike the scalar outputs, the vector field outputs are listed individually in the Output scroll box. Allowed destinations for vector field output are running instances of mmDisp and mmArchive. Caution is advised when scheduling vector field output, especially with large problems, because the output may run many megabytes.
Controls
The File menu button holds five entries: Load, Show Console, Close
Interface, Clear Schedule and Exit Oxsii. File|Load...
launches a dialog box that allows the user to select an input MIF problem description file. File|Show Console brings up a
Tcl shell console running off the Oxsii interface Tcl interpreter. This console is intended primary for debugging purposes.
In particular, output from
MIF Report commands
may be viewed here. File|Close Interface will remove the
interface window from the display, but leaves the solver running. This
effect may also be obtained by deselecting the
Oxsii interface button in the Threads list in
mmLaunch.
File|Clear Schedule will disable all currently active
output schedules, exactly as if the user clicked through the interactive
schedule interface one output and destination at a time and disabled
each schedule-enabling checkbutton.
The final entry,
File|Exit Oxsii, terminates the Oxsii solver and closes the
interface window.
The Options menu holds two entries: Clear Schedule and Restart Flag. The first clears all Step and Stage selections from the active output schedules, exactly as if the user clicked through the interactive schedule interface one output and destination at a time and disabled each schedule-enabling checkbutton. This control can be used after loading a problem to override the effect of any Schedule commands in the MIF file. The restart flag controls problem load behavior. In normal usage, the restart flag is not set and the selected problem loads and runs from the beginning. Conversely, if the restart flag is set, then when a problem is loaded a check is made for a restart (checkpoint) file. If the checkpoint file is not found, then an error is raised. Otherwise, the information in the checkpoint file is used to resume the problem from the state saved in that file. The restart flag can be set from the Options menu, the File|Load dialog box, or from the command line. See the Oxs_Driver documentation for information on checkpoint files.
The Help menu provides the usual help facilities.
The row of buttons immediately below the menu bar provides simulation progress control. These buttons become active once a problem has been loaded. The first button, Reload, re-reads the most recent problem MIF input file, re-initializes the solver, and pauses. Reset is similar, except the file is not re-read. The remaining four buttons, Run, Relax, Step and Pause place the solver into one of four run-states. In the Pause state, the solver sits idle awaiting further instructions. If Step is selected, then the solver will move forward one iteration and then Pause. In Relax mode, the solver takes at least one step, and then runs until it reaches a stage boundary, at which point the solver is paused. In Run mode, the solver runs until the end of the problem is reached. Interactive output is available in all modes; the scheduled outputs occur appropriately as the step and stage counts advance.
Directly below the progress control buttons are two display lines, showing the name of the input MIF file and the current run-state. Below the run-state Status line is the stage display and control bar. The simulation stage may be changed at any time by dragging the scroll bar or by typing the desired stage number into the text display box to the left of the scroll bar. Valid stage numbers are integers from 0 to N - 1 , where N is the number of stages specified by the MIF input file.
Details
The simulation model construction is governed by the Specify blocks in
the input MIF file. Therefore, all aspects of the simulation are
determined by the specified
Oxs_Ext classes.
Refer to the appropriate Oxs_Ext class documentation for simulation and
computational details.
Known Bugs
A bug in the network traffic handling code of
Tcl on Windows 9X systems can sometimes interfere
with communications between the control interface of Oxsii and
the actual computation engine. If Oxsii is sending out data
to two or more data display services every iteration, the network
traffic from that data can ``crowd out'' the receipt of
control messages from the control interface. You may observe this as a
long delay between the time you click the Pause button and the
time the solver stops iterating. This bug first appeared in Tcl release 8.0.3, and remained through Tcl release 8.1.1. It is fixed in
Tcl releases 8.2 and later, which we recommend for OOMMF users on
Windows 9X systems. Other platforms do not have this problem.
If Tcl version 7.5 is in use, and Oxsii processes a Destination command in a MIF file, and in response launches another application, then Oxsii will not be able to fully terminate until the launched application also terminates. You might notice this in mmLaunch where an Oxsii will remain in the Threads column long after it has apparently exited. This glitch is due to a bug in Tcl's exec command in version 7.5 that has long been fixed. Use a more recent Tcl release to avoid the problem.
